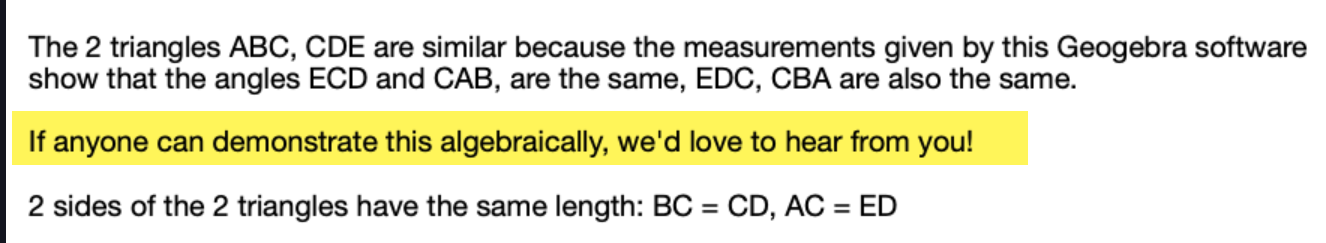Hush : More information about the Kepler right triangle revealed part 1:
Some of the properties of the Kepler right triangle:
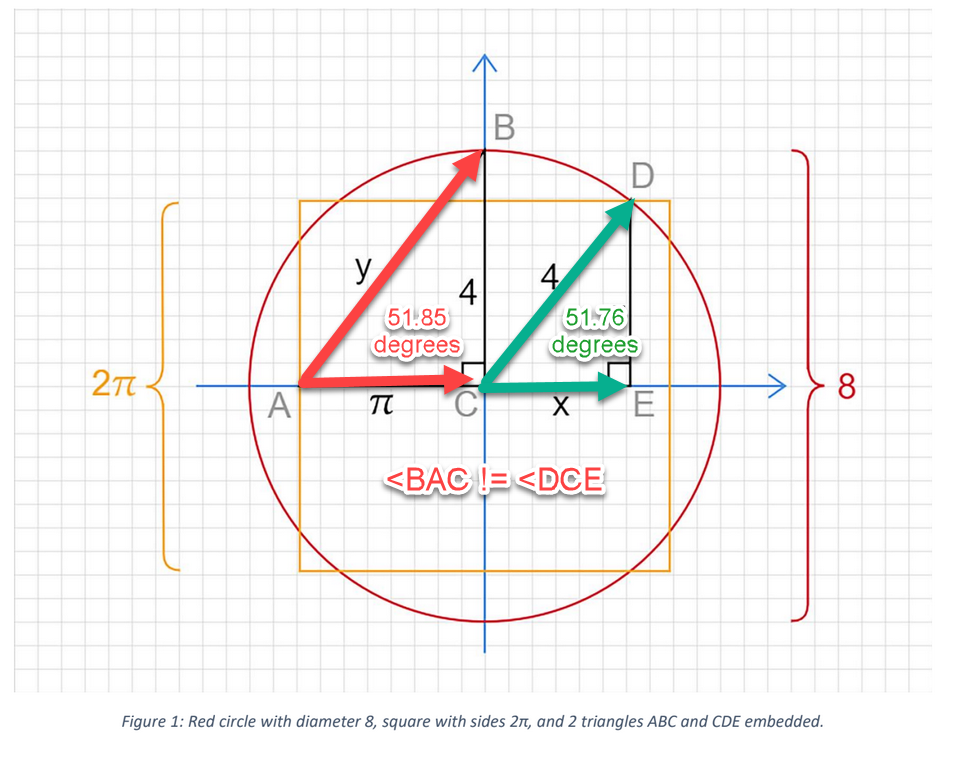
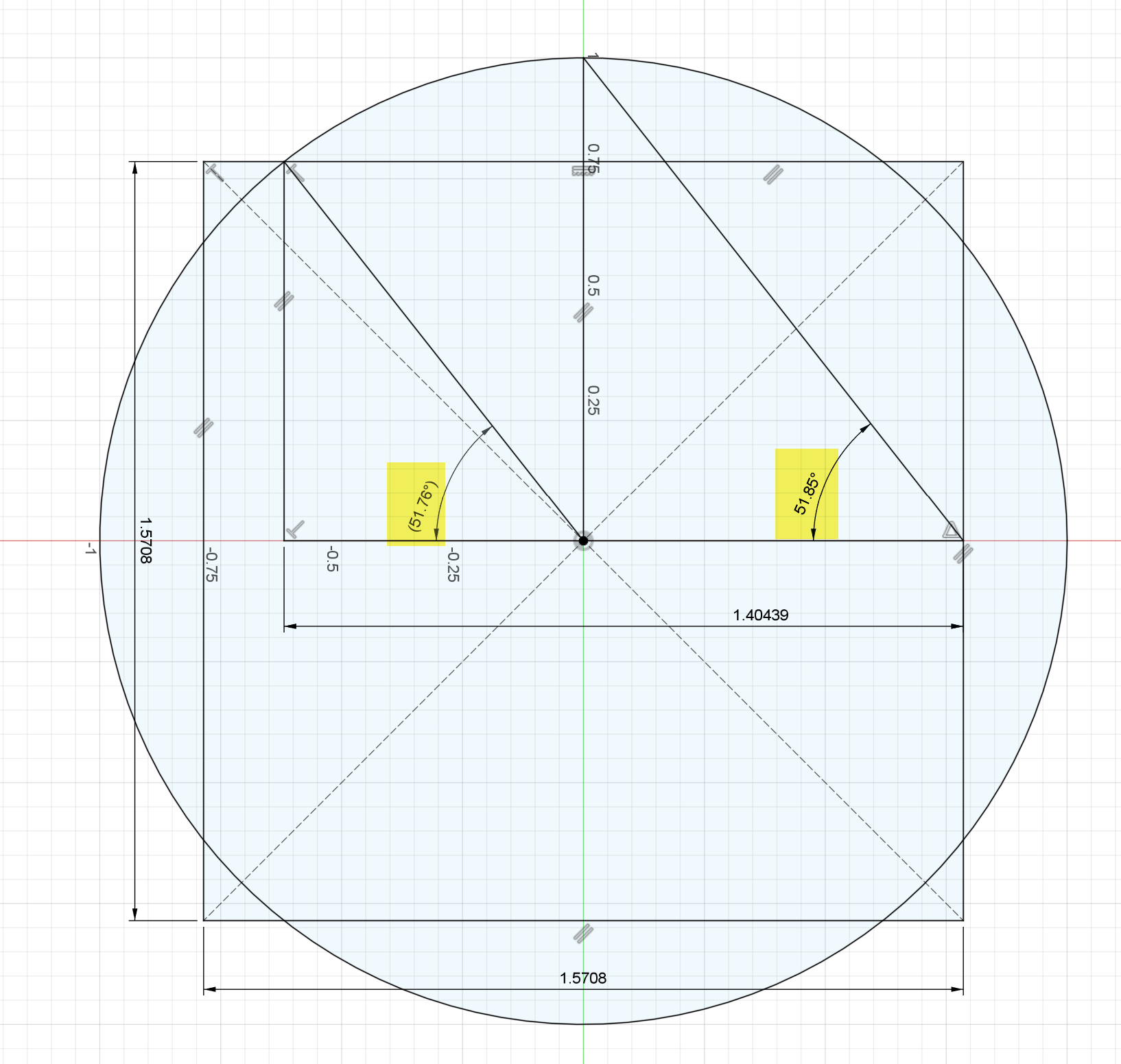
The measuring angles for the hypotenuse of a Kepler right scalene triangle are (ATAN(√φ)) = 51.82729237298776 degrees and (ATAN(1/(√φ)) = 38.17270762701224 degrees in Trigonometry.
(ATAN(√φ)) = 51.82729237298776 degrees is gained when the ratio √φ = 1.272019649514069 is applied to the inverse of the Tangent function in Trigonometry.
38.17270762701226 degrees is gained when the ratio (1/(√φ)) = 0.786151377757423 is applied to the inverse of the Tangent function in Trigonometry.
If the hypotenuse of a Kepler scalene right triangle is divided by the shortest edge length of the Kepler scalene right triangle then the resulting ratio is The Golden ratio of cosine (36 degrees) multiplied by 2 = (φ) = (√(5) plus 1)/2 = 1.618033988749895.
√φ = 1.27201964951406 is the ratio gained from dividing the second longest length of a Kepler scalene right triangle by the shortest edge length of the Kepler right scalene triangle.
√φ = 1.27201964951406 is also the Golden ratio of cosine (36 degrees) multiplied by 2 = (φ) = (√(5) plus 1)/2 = 1.618033988749895.
The Kepler right triangle is the solution to:
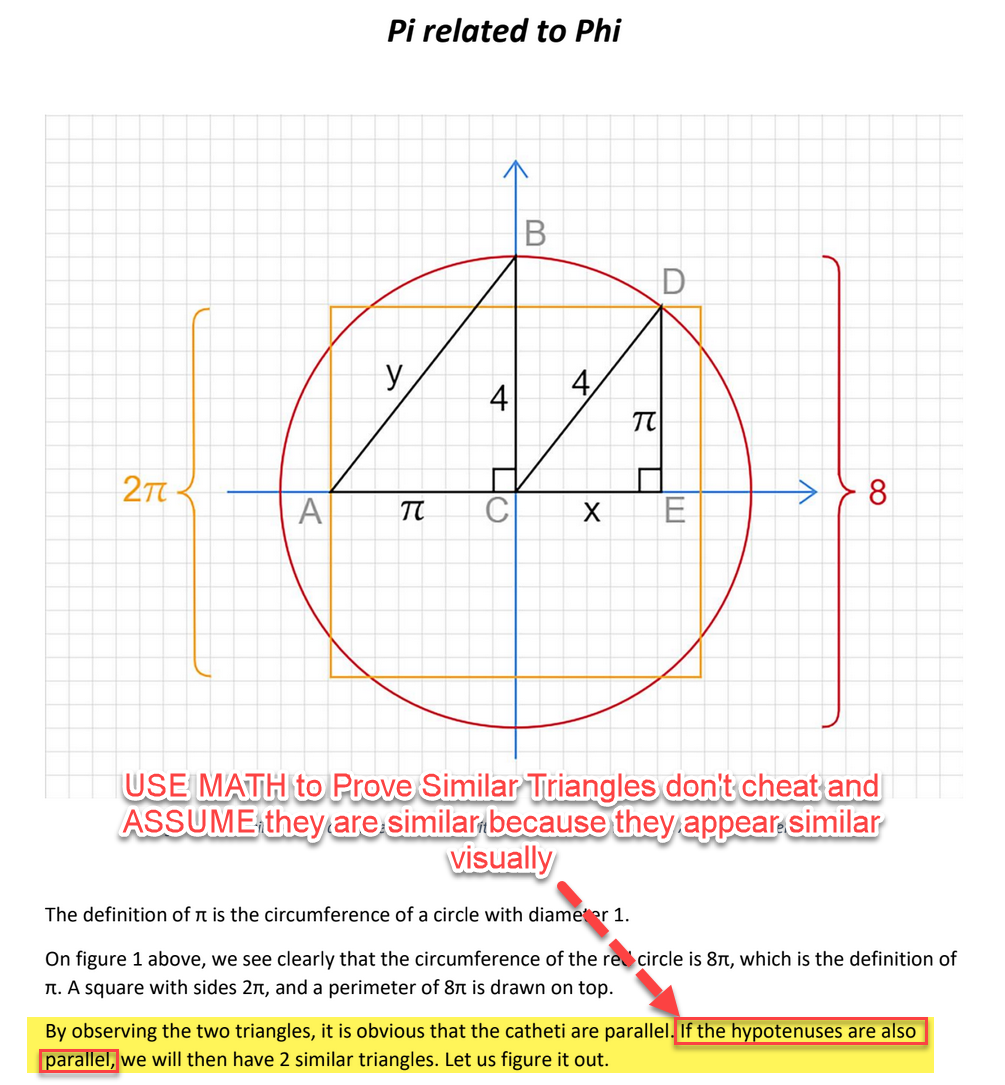
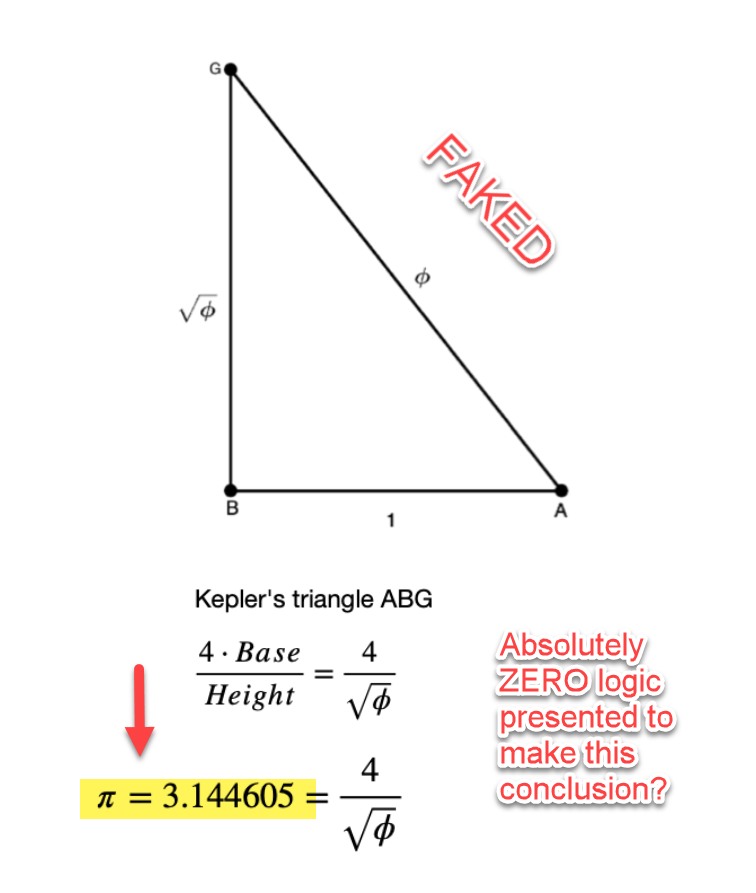
Discovering the correct value for 𝝿 = Pi = 4/√φ = 3.144605511029693144.
Creating a circle and a square with the same surface area by using just compass and straight edge.
Creating a circle and a square with equal perimeters by using just compass and straight edge.
- Creating an Equilateral triangle and a circle with equal perimeters by using just compass and straight edge.
- Creating an Equilateral triangle and a circle with he same surface area by using just compass and straight edge.
- Creating a Pentagon and a circle with equal perimeters by using just compass and straight edge.
- Creating a Pentagon and a circle with the same surface area by using just compass and straight edge.
- Creating a Cube and a sphere with the same surface area by using just compass and straight edge.
- Creating a Cube and sphere with the same volume.
10.Creating a Phi Pyramid and a sphere with the same surface area by using just compass and straight edge.
11.Creating a Phi Pyramid and a sphere with the same volume.
- Creating a Locun ratio Pyramid and a sphere with the same surface area by using just compass and straight edge.
- Creating a Locun ratio Pyramid and a sphere with the same volume.
More information about the Kepler right triangle revealed part 2:
More information about the Kepler right triangle revealed:
The measuring angles for the hypotenuse of a Kepler right scalene triangle are ATAN(√φ) = 51.82729237298776 degrees and ATAN(1/(√φ)) = 38.17270762701224 degrees in Trigonometry.
ATAN(√φ) = 51.82729237298776 degrees is gained when the ratio √φ = 1.272019649514069 is applied to the inverse of the Tangent function in Trigonometry.
38.17270762701226 degrees is gained when the ratio (1/(√φ)) = 0.786151377757423 is applied to the inverse of the Tangent function in Trigonometry.
If the hypotenuse of a Kepler scalene right triangle is divided by the shortest edge length of the Kepler scalene right triangle then the resulting ratio is The Golden ratio of cosine (36 degrees) multiplied by 2 = (φ) = (√(5) plus 1)/2 = 1.618033988749895.
√φ = 1.27201964951406 is the ratio gained from dividing the second longest length of a Kepler scalene right triangle by the shortest edge length of the Kepler right scalene triangle.
√φ = 1.27201964951406 is also the Golden ratio of cosine (36 degrees) multiplied by 2 = (φ) = (√(5) plus 1)/2 = 1.618033988749895.
A Kepler right scalene right triangle can allow a circle with a circumference equal to the perimeter of a square to be created.
If a circle and a square are created with equal perimeters of measure than half the perimeter of the square divided by the radius of the circle is Pi and if either the perimeter of the square or the circumference of the circle is divided by the diameter of the circle then the resulting ratio is Pi.
Also if a circle and a square are created with equal perimeters of measure and the width of the square is divided by the radius of the circle then the resulting ratio is half of Pi = 2/√φ = 1.572302755514847.
The ratio 2/√φ = 1.572302755514847 half of Pi can be gained from 2 divided by the square root of (φ) = 1.618033988749895 = (√φ = 1.27201964951406).
If the hypotenuse of a Kepler scalene right triangle is divided by the shortest edge length of the Kepler scalene right triangle then the resulting ratio is the Golden ratio of cosine (36 degrees) multiplied by 2 = (φ) = (√(5) plus 1)/2 = 1.618033988749895.
√φ = 1.27201964951406 is the ratio gained from dividing the second longest length of a Kepler scalene right triangle by the shortest edge length of the Kepler right scalene triangle.
√φ = 1.27201964951406 is also the square root of the Golden ratio of cosine (36 degrees) multiplied by 2 = (φ) = (√(5) plus 1)/2 = 1.618033988749895.
Please remember that if the second longest edge length of a Kepler right triangle is divided by 1 quarter of the shortest edge of a Kepler right triangle the result is the ratio 4 times the square root of the Golden ratio = (4 times √φ) = 5.088078598056276.
The square root of the Golden ratio = √φ = 1.272019649514069. √φ = 1.272019649514069 multiplied by 4 = the ratio 5.088078598056276.
Please remember that if the hypotenuse a Kepler right triangle is divided by 1 quarter of the second longest edge length of a Kepler right triangle the result is the ratio 4 times the square root of the Golden ratio (4 times √φ) = 5.088078598056276.
The square root of the Golden ratio = √φ = 1.272019649514069. √φ = 1.272019649514069 multiplied by 4 = (4 times √φ) = 5.088078598056276.
If a circle and a square are created and the perimeter of the square is the same measure as the circumference of the circle and the circle’s circumference is divided by the circumference of another circle that has a diameter that is the same measure as the width of the square then the result is the square root of the Golden ratio = √φ = 1.27201964951406.
If a circle and a square are created with the same surface area and the circumference of the circle is divided by the circumference of another circle that has the same measure as the width of the square then the result is the square root of the square root of the Golden ratio = √√φ = 1.127838485561682.
Please remember that the ratio √√φ = 1.127838485561682 is the square root of the ratio √φ = 1.272019649514069 and the ratio √φ = 1.272019649514069 is the square root of the Golden ratio of cosine (36 degrees) multiplied by 2 = (φ) = (√(5) plus 1)/2 = 1.618033988749895.
If the shortest edge length an Illumien right triangle is reduced to 1 then the second longest edge length of the Illumien right triangle is equal to the square root of the square root of the Golden ratio = √√φ = 1.127838485561682.
If the shortest edge length an Illumien right triangle is reduced to 1 then the hypotenuse of the Illumien right triangle is equal to the Locun ratio = the square root of 2.272019649514069 = (√(√φ plus 1)) = 1.507322012548768.
If the second longest edge length of an Illumien right triangle is divided by 1 quarter of the shortest edge length of an Illumien right triangle the result is the ratio = (4 times √√φ) = 4.511353942246728. (4 times √√φ) the ratio 4.511353942246728 is 4 times the square root of the square root of the Golden ratio = 1.127838485561682.
The ratio √√φ = 1.127838485561682 multiplied by 4 = (4 times √√φ) = 4.511353942246728.
A circle with a radius equal to (4 times √√φ) = 4.511353942246729 equal units of measure has a surface area of 64 equal units of measure according to Golden Pi = 4 divided by the square root of Phi = 4/√φ = 3.144605511029693.
8 squared = 64.
Please remember that the ratio √√φ = 1.127838485561682 is the square root of the ratio √φ = 1.272019649514069 and the ratio √φ = 1.272019649514069 is the square root of the Golden ratio of cosine (36 degrees) multiplied by 2 = (φ) = (√(5) plus 1)/2 = 1.618033988749895. If 4500 is multiplied by the ratio √φ = 1.272019649514069 the result is 5724.0884228133105. (5724).
Repeat: 4500 times √φ = 1.272019649514069 = the ratio 5724.0884228133105 is the radius of a circle with a circumference of 36000 equal units of measure according to Golden 𝝿 = Pi = 4/√φ = 3.144605511029693144 and Golden Tau = 8/√φ = 6.289211022059386.
Constants that unify and alter space and time. The Quadrature of the circle constants:
The Golden ratio of cosine (36 degrees) multiplied by 2 = (φ) = (√(5) plus 1)/2 = 1.618033988749895.
(Phi = (2/((√(5) subtract 1))) = The Golden ratio = 1.618033988749895).
(φ plus 2) = 3.618033988749895. ((2/((√(5) subtract 1))) plus 2) = 3.618033988749895
(√(φ plus 2)) = 1.902113032590307. (cosine (18 degrees) multiplied by 2) = 1.902113032590307.
√φ = 1.272019649514068.
√√φ = 1.127838485561682.
Golden 𝝿 = Pi = 4/√φ = 3.144605511029693144.
Half of Golden Pi = 2/√φ = 1.572302755514847.
(√(1 plus (√φ)) = 1.507322012548768. √(√φ plus 1)) = 1.507322012548768.
((√(√φ plus 1)) plus 1) = 2.507322012548768.
(1 plus √φ) = 2.272019649514069. (√φ plus 1) = 2.272019649514069.
(2 plus √φ) = 3.272019649514069. (√φ plus 2) = 3.272019649514069.
(√(2 plus √φ)) = 1.808872480169365. (√(√φ plus 2)) = 1.808872480169365.
(2/(√√(3 times φ))) = 1.347419325335723.
√((34 times 17 times TAN(54)/2 times 5)) times √√φ/(34) = 1.479351567442321.
(√(1.5 times √φ)) = 1.381314400949727.
(1.5 times √φ) ^ (1/3) = 1.240304615214716.
(φ times √√φ) = 1.824881003459009.
(φ times √√φ/√φ) = 1.43463271511265.
(2/√φ) ^ (1/3) = 1.162818837094896.
(√(√(√(φ) plus 1) plus 1)) = 1.583452560877265.
(2 ^ (1/3)) = 1.259921049894873.
(√√φ times (2 ^ (1/3))) = 1.420987448840718.
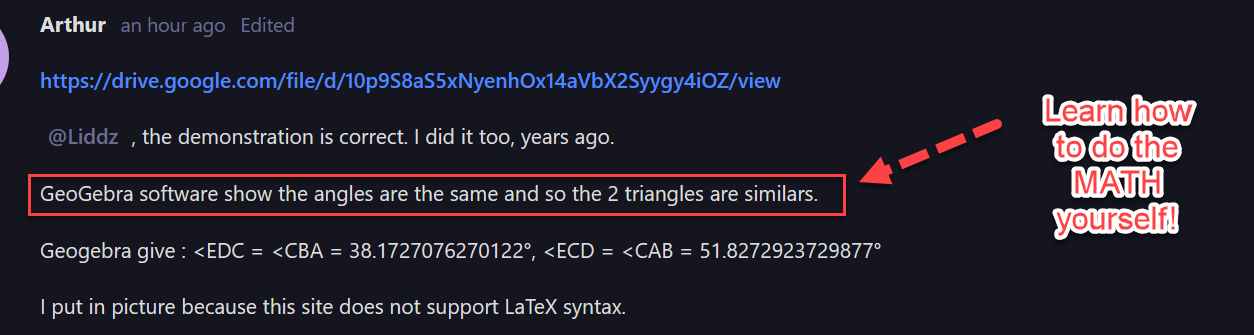
The proof above is correct because both of the right triangles are Kepler right triangles.
The measuring angles for the hypotenuse of a Kepler right scalene triangle are ATAN(√φ) = 51.82729237298776 degrees and ATAN(1/(√φ)) = 38.17270762701224 degrees in Trigonometry.
ATAN(√φ) = 51.82729237298776 degrees is gained when the ratio √φ = 1.272019649514069 is applied to the inverse of the Tangent function in Trigonometry.
38.17270762701226 degrees is gained when the ratio (1/(√φ)) = 0.786151377757423 is applied to the inverse of the Tangent function in Trigonometry.
If the hypotenuse of a Kepler scalene right triangle is divided by the shortest edge length of the Kepler scalene right triangle then the resulting ratio is The Golden ratio of cosine (36 degrees) multiplied by 2 = (φ) = (√(5) plus 1)/2 = 1.618033988749895.
√φ = 1.27201964951406 is the ratio gained from dividing the second longest length of a Kepler scalene right triangle by the shortest edge length of the Kepler right scalene triangle.
√φ = 1.27201964951406 is also the Golden ratio of cosine (36 degrees) multiplied by 2 = (φ) = (√(5) plus 1)/2 = 1.618033988749895.
ATAN(√φ) degrees = 51.82729237298776 degrees rounded off to 51.83 degrees.
Please click on the Wolfram alpha link below to confirm the truth of my claims.
ATAN(√φ) degrees:
https://www.wolframalpha.com/input?i=ATAN%28%E2%88%9A%CF%86%29+degrees




 .
.